Cannabis Cultivation: A Closer Look at its Agricultural Potential
Cannabis, once relegated to the shadows, is emerging as a mainstream agricultural crop with the potential to revolutionize farming practices.
1. Historical Context:
Cannabis has a rich history of cultivation dating back centuries. The recent shift in perception and legalization has brought cannabis into the spotlight, prompting a reevaluation of its role in #agriculture.
2. Cultivation Techniques:
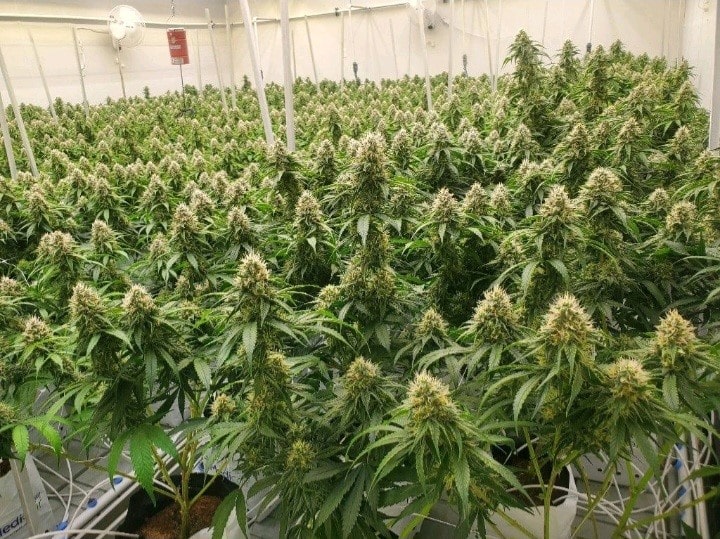
Skilled growers employ advanced cultivation techniques to optimize cannabis yields and quality. From selecting the right strains to implementing precise nutrient regimens and controlled environments, these experts treat cannabis much like any other high-value crop.
3. Biodiversity & Genetic Variation:
The cannabis plant boasts a diverse array of strains, each with unique characteristics. Skilled growers focus on preserving and enhancing this genetic diversity, recognizing the importance of resilient and adaptable plants in the face of changing environmental conditions.
4. Environmental Impact:
Contrary to misconceptions, cannabis cultivation can be environmentally sustainable. Expert growers leverage innovative methods such as vertical farming, aquaponics, and organic practices to minimize the ecological footprint, showcasing the plant’s potential to coexist harmoniously with nature.
5. Economic Contributions:
As cannabis gains acceptance, its economic significance cannot be understated. Skilled cultivators contribute to job creation, local economies, & the development of a burgeoning industry. This economic impact echoes the role of other agricultural crops in shaping regional prosperity.
6. Challenges & Regulations:
Despite its potential, cannabis cultivation faces regulatory challenges in various regions. Skilled growers navigate these hurdles, advocating for responsible & informed legislation that recognizes the agricultural nature of cannabis and promotes sustainable practices.
7. Technological Integration:
The integration of technology in cannabis cultivation is a hallmark of skilled growers. Automation, data analytics, & precision agriculture techniques are harnessed to optimize resource use, enhance crop monitoring, and ensure consistent, high-quality yields.
8. Educational Initiatives:
To foster responsible cultivation practices, skilled growers actively engage in educational initiatives. Sharing knowledge on sustainable farming, genetics, & best practices not only benefits the industry but also demystifies cannabis cultivation for the broader public.
In the hands of skilled growers, cannabis transcends its historical stigmas to become just another agricultural plant—albeit one with unique characteristics and applications.
As society continues to embrace the plant’s potential, the expertise of cultivators will play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable and thriving cannabis agricultural sector.
Cannabis, another crop in the hands of skilled growers?











Leave a Reply